What is the Project Management Professional (PMP) Certification

The PMP exam is administered by the Project Management Institute (PMI). The exam is based on the PMP Examination Specification, which describes tasks/activities from five performance domains:
-
- Initiation (13%)
- Planning (24%)
- Executing (30%)
- Monitoring and controlling (25%)
- Closing (8%)
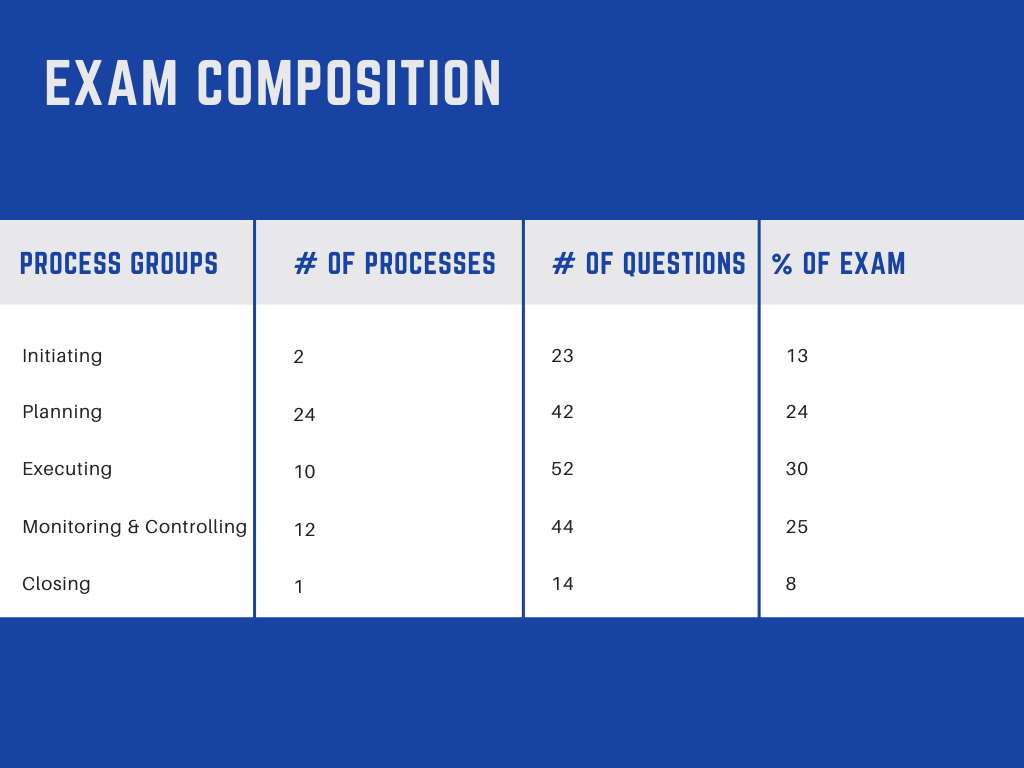
The exam consists of 200 multiple choice questions based on the PMBOK specification and the PMP Code of Ethics.
The exam is a closed-book one with no reference materials allowed. The only reference materials allowed are your brain-dumps (allowed on the materials you are given to do rough sketches when the proctor checks you into the exam center).
Twenty-five of the 200 questions on the exam are seeded “sample” questions. These questions are used to test their level of difficulty and quality to determine if they should be added to the PMI’s questions base. The seeded questions do not count against you as a test taker. These questions are placed randomly throughout the exam. The test taker is only graded on their proficiency in the remaining 175 questions.
The numbers in parentheses describe the percentage of questions for each domain.
PMI announced in June 2019 that the PMP Examination Content Outline will undergo significant re-categorization, effective January 2021. This will suggest 3 all-new performance domains:
-
- People (42%)
- Process (50%)
- Business Environment (8%)
Item references
An exam question with its possible answer choices has at least two references to standard books or other sources of project management. Most of the questions reference the PMI A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (otherwise known as the PMBOK Guide) which is currently in its sixth edition (2018). The PMP exam changed in March 2018 to align with the updated guide.
The Project Management Framework embodies a project life cycle and five major project management Process Groups including:
-
- Initiating
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Closing
There are ten project management Knowledge Areas mapped to the process groups and they include:
-
- Project Integration Management
- Project Scope Management
- Project Schedule Management
- Project Cost Management
- Project Quality Management
- Project Resource Management
- Project Communications Management
- Project Risk Management
- Project Procurement Management
- Project Stakeholder Management
The process groups and Knowledge Areas are parents to a total of 49 processes.
These processes are described by i) what they are, ii) why they are performed, and iii) when they are performed. They are also described by their inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs.
The PMBOK emphasizes the importance of tailoring based on project needs, environments, and other prevailing constraints. It additionally emphasizes how different process groups interact and rely on each other.
Examples include:
- Defining the dependency between the process groups on a project based on the project constraints.
- The output of a particular process as an input to another process. E.g. Validated Deliverable as an output of Control Quality process and an input of Validate Scope process
Purpose
Non-Profits, government, and other organizations rely on PMP certified project managers to improve the success rate of their projects. PMP certified project managers achieve this by applying their knowledge of the standardized and evolving set of project management principles contained in the PMBoK Guide.
The project management certification is among the topmost in-demand certifications according to Business News Daily. Project Management Professional (PMP®) certifications have soared in value between 2018 to today, jumping 25% from a median salary of $114,473 in 2018 to $143,493 in 2020 according to Forbes. The PMP credential was ranked as a top certification by CIO in 2020. The PMP credential has also been ranked as one of the top certifications by Global Knowledge, behind Cloud and Security certifications in 2020.
Examination process
Pearson VUE testing centers provide the PMP exam as a computer-based test either at a test center or remotely. They are administered with the supervision of proctors.
They also offer a paper-based option for locations with no nearby Prometric testing centers(). The exam consists of 200 questions. 25 are seeded questions, which are not included in exam grading. The overall score is based on the other 175 questions. Each multiple-choice question has one correct answer and three incorrect answers. There is no penalty for an incorrect answer.
As noted earlier, the examination can now be taken from home or an office location as extra options to sitting for the exams at the testing center.
There will be a live proctor and the requirements include a quiet environment, a reliable internet connection and a computer with a webcam.
Candidates who take the computer-based test receive their results (passed or not passed) on the screen immediately upon completion using PMI’s 4 proficiency levels (Above Target, Target, Below Target, and Needs Improvement) in each project management process group.
The proctors provide the exam results to the candidate on a score report after the examination. Candidates who take paper-based tests receive their test results and score reports typically within 4 weeks.
Research shows that the most difficult knowledge areas of the PMP exam are Quality Management, Integration Management, and Schedule Management.
PMI Audit
Random Audits are PMI’s modus operandi to verify the experience and/or education claims by certification candidates. This is done to maintain the integrity and standing of PMI as a body and the PMP certification and all other associated certifications.
Item writing
Item writing is used to add new questions to the PMP Examination database while other questions are taken off using project management guides and texts as guides. Instructors, course developers, book authors, and other individuals who are active in the field of PMP exam education are not allowed to conduct item writing.
Eligibility Requirements
Candidates must meet the prerequisites in one of the following groups to be eligible for PMP Certification:
Group A
- Secondary degree (high school diploma, associate degree or the global equivalent)
- 7,500 hours leading and directing projects
- 60 months
- 35 contact hours of project management education
Group B
- Four-year degree
- 4,500 hours leading and directing projects
- 36 months
- 35 contact hours of project management education
Continuous Credential Requirements (CCRs) require Professional Development Units (PDUs)
Project Management Professionals (PMPs) require a total of 60 Professional Development Units (PDUs) every 3-year Cycle to maintain their PMP certifications.
The following activities qualify as PDUs
- Creating educational content on project management topics using articles, videos
- Speaking at project management events
- Practicing as a project manager
- Attending project management training or courses
- Research in the field of project management
The PDUs must satisfy the components of the PMI Talent Triangle (technical, leadership, and strategic and business management expertise).
Other PMI credentials
PMP (Project Management Professional) is one of nine credentials offered by PMI:
- Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM)
- Project Management Professional (PMP)
- Program Management Professional (PgMP)
- PMI Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP)
- Disciplined Agile
- PMI Risk Management Professional (PMI-RMP)
- PMI Scheduling Professional (PMI-SP)
- Portfolio Management Professional (PfMP)
- PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PMI-PBA)



