Project Management Professional (PMP) Performance Domains/Process Groups Overview

While Studying for the PMP certification, it is important that students know they are currently being tested under 5 Performance Domains/Process Groups which include:
- Initiating
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring & Controlling
- Closing
The exam questions are drawn from Tasks that make up each performance domain. The examination will test your proficiency with these Tasks.
Below is the breakdown of the Performance Domains/Process Groups and the number of Tasks and Process they are composed of.
- Initiating – 8 Tasks – 2 Processes
This Domain contains Tasks/Activities that deal with defining/understanding the project scope, identifying stakeholders and obtaining approval from them.
2. Planning – 13 Tasks – 24 Processes
This Domain includes Tasks/Activities that are useful for developing projects plans for Scope, Requirements, Change, Schedule, Cost, Quality, Resource, Communication, Risk, Procurement and Stakeholder management portions of the project.
3. Executing – 7 Tasks – 10 Processes
This Domain includes the Tasks/Activities that are needed for doing the work required to deliver the project objectives.
4. Monitoring & Controlling – 7 Tasks – 12 Processes
This Domain includes Tasks/Activities that ensure that project objectives are realized through effective scope, change, progress, risk, quality and status management.
5. Closing – 6 Tasks – 1 Process
This Domain contain Tasks/Activities completing phase or final project work, obtaining deliverables acceptance by customers, completing all phase or project closure documents, archiving important project documents and communicating project closure to relevant stakeholders.
You can read more about the Tasks associated with the Performance Domains/Process Groups here.
In total, the PMP Process Map is made up of 49 Processes as shown in the Table below. More information can be found in the Project Management Body of Knowledge Guide (6th Edition).
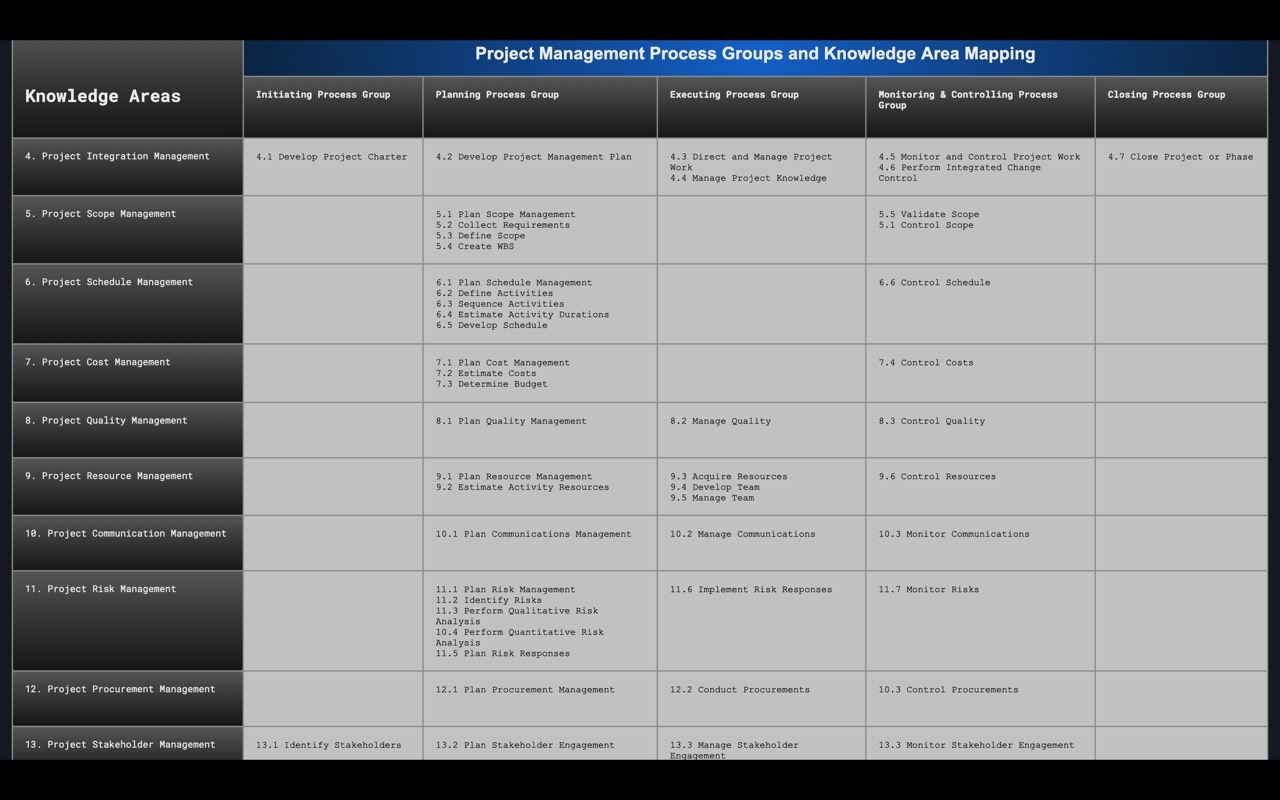
INPUTS, TOOLS & TECHNIQUES AND OUTPUTS (ITTOs)
Inputs, Tools & Techniques and Outputs (ITTOs) constitute the building block of each process. As a PMP aspirant, you will need to have a solid understanding of the flow of the ITTOs for all the processes.
- INPUTS
An INPUT is any item, whether within or outside the project environment, which is required before the process starts. It may be an output from a predecessor process.
Common inputs include:
- Organizational Process Assets
- Enterprise Environmental Factor (Internal & External):
- Project Management Plan
- Project Documents
- Work Performance Data
- Work Performance Information
2. TOOLS & TECHNIQUES
Tool (Noun): Something tangible, such as template or software program used in performing a task to produce a product, result or service.
Technique (Verb): A procedure employed by a human resource to perform a task to produce a product, result or service and that may use one or more tools.
Some common Tools and Techniques:
- Data Gathering
- Data Representation
- Data Analysis
- Communication
- Decision Making
- Estimating
- Interpersonal and Team Skills
- Project Management Information System (PMIS)
- Expert Judgement
- Meetings
3. OUTPUTS
An output is a product, service or result generated at the end of a process. It could be an input to a successor process.
Examples are:
- Organizational Process Assets Updates
- Enterprise Environmental Factors Updates
- Project Documents Updates
- Project Management Plan Updates
- Work Performance Information
- Work Performance Report
- Change Requests
Outputs of a process could be inputs to other processes.
In summary, as an aspiring PMP candidate, you must understand the Performance Domains/Process Groups, their component Tasks, Processes and their respective Inputs, tools & techniques and outputs flow.



